Gastrointestinal Microbiota & Reproducibility of Animal Disease Models
Differences in gastrointestinal microbiota contribute to phenotypic variance in experimental disease models, lowering the reproducibility of many preclinical animal model studies. As experts in conducting preclinical animal model experiments, Chondrex, Inc. can help you identify sources of microbial variation in your experiments, as well as make a few recommendations to increase the reproducibility of your experiments. Continue reading to find out how to limit gastrointestinal microbiota variance in your experimental disease model experiments! Read More

Immune Complexes Drive Pre-Inflammatory Pain in Collagen Antibody-Induced Arthritis Model
Pain-like behavior has been observed before the onset of inflammation in the Collagen Antibody-Induced Arthritis model. This new pain mechanism does not utilize traditional inflammatory pain pathways. Instead, the pain-like behavior seems to be induced by direct neuron activation by type II collagen-autoantibody immune complexes. More research is needed to determine how this finding translates to human disease, but it could provide a avenue of treatments for chronic pain in autoimmune disease patients. Read More

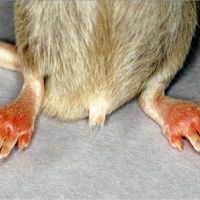
Spontaneous Arthritis Development in LPS-Induced Periodontitis Model
For the first time, it has been reported that a LPS-induced periodontitis model led to the spontaneous development of arthritis in CD-1 mice. These findings further strengthen the link between periodontal disease and rheumatoid arthritis, while highlighting the potential role of the gastrointestinal microbiome in perpetuating inflammatory responses. Moving forward, it will be vital to consider the immune interactions between the host and the microbiome when researching systemic inflammatory diseases so we may gain a better understanding of seemingly idiopathic autoimmune diseases. Read More
Anti-Bacteria Antibody ELISAs as Analytical Tool in Autoimmune Disease Research
A recent paper sought to evaluate the usefulness of several bacteriological and serological analytical methods in evaluating the triggering bacteria of spondyloarthritis. Serological evaluation by assaying for antibodies against specific bacteria provides a glimpse of a patient's previous exposure to potential pathogenic bacteria, while also providing information on the patients immune response to that bacteria. Anti-Bacteria Antibody Assays kits are therefore a very useful tool for researchers and clinicians alike to study the complex mechanisms underlying spondyloarthritis and other autoimmune diseases. Read More

Optical Molecular Imaging Inflammation in Mouse CAIA Model
There is currently a need for a cost-effective imaging technique to aid in the early diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis, a crucial factor in improving patient outcomes. Optical molecular imaging (OMI) is currently used to image tumors for diagnostic and surgical applications, but can be adapted for imaging cellular and sub-cellular processes that are a part of other diseases. This article reviews how researchers at the University of Michigan used OMI to image inflammation in the mouse CAIA model, with promising implications for clinical usage. Read More

Troubleshooting the Collagen-Induced Arthritis Model
While the Collagen-Induced Arthritis model is the most popular rheumatoid arthritis model, there are many sources of variation that can alter the development of the model. Here is a list of factors to consider when planning a CIA experiment in order to reduce sources of variation and increase the reproducibility of your model. Read More

Microbiota: Linking Genetics and Inflammatory Disease
Humans and the microbiota living in an on human surfaces (microbiota) have co-evolved over thousands of years, affecting each other's development in unknown ways. While microbes have traditionally been viewed as having a commensal or parasitic relationship with their hosts, a surge in microbiota research is showing how important microbiota is for human health (1,2). Colonization of human mucosal surfaces... Read More

Krüppel-Like Factor 4: New Target for Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment
KLF4 has been identified as a potential therapeutic target for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients whose symptoms cannot be managed with current treatments. This blog highlights how the modulatory role of KLF4 in RA was determined using well-characterized disease models: Collage-Induced Arthritis and Collagen Antibody-Induced Arthritis. Read More

Arthritis Models: Using CIA and CAIA to Study RA GWAS Risk Loci
Genome Wide Association Studies (GWASs) have identified numerous genes as potential therapeutic targets for rheumatoid arthritis and other autoimmune diseases. However, determining the roles of these genetic factors in RA pathogenesis is virtually impossible. Therefore, the mouse Collagen-Induced Arthritis and Collagen Antibody-Induced Arthritis models are useful tools to parse a genetics mechanisms for autoimmune arthritis. Read More

Intestinal Bacteria Modulate Inflammatory Arthritis
Review of paper published by W.K. Jubair et al. which analyzes how intestinal microbiota changes during the development Collagen-Induced Arthritis in mice. The study continues by using broad-spectrum antibiotics to observe the time-dependent effects that microbiota exert on autoimmunity. Read More
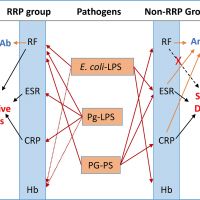
Different Bacterial Pathogens May Affect Serological Disease Markers in RRP and non-RRP Rheumatoid Arthritis
Summary of Terato et al. (2018) which studied correlations between antibody responses to common bacterial pathogens (E. coli LPS, P. gingivalis LPS, and peptioglycan-polysaccharide) and rheumatoid arthritis disease markers. The results suggest that different bacterial pathogens may be involved in evoking serological disease markers in RRP and non-RRP rheumatoid arthritis, and may contribute to the different disease outcomes in these patient groups. This paper lays the groundwork for studying rheumatoid arthritis and other autoimmune diseases as perturbations of gastrointestinal bacterial populations rather than a malfunctioning immune response. Read More

New Product: MTT Cell Proliferation and Viability Assay Kit
Since its creation in 1983 (1), the MTT assay has been widely used for assaying cell viability, proliferation, and measuring the cytotoxicity of test compounds. MTT is one of several tetrazolium salts that have been used for assessing metabolic activity of cells, however it is the only one that is positively charged and therefore can readily be taken up by... Read More

Bifidobacterium infantis reduces inflammation in mouse models of asthma and food allergies
A study conducted at Shenzhen Children's Hospital demonstrates how oral feeding of B. infantis can reduce signs of inflammation in ovalbumin-induced asthma and β-lactoglobulin-induced food allergy in mice. This study adds to a growing body of research suggesting that manipulation of gut microbiota is a viable treatment for allergies and autoimmune diseases. Read More

Influence of Diet and Probiotic Bacteria on Intestinal Barrier Function
The permeability of the intestinal epithelial barrier plays a significant role in an individual's systemic exposure to LPS and other bacterial toxins. The complex relationship between diet and intestinal permeability is not entirely clear, however the article reviewed here presents evidence that a probiotic bacteria, L. gasseri SBT2055, may be able to improve intestinal permeability. This research can lead to new strategies for treating metabolic disorders like obesity. Read More

Introduction to Exosomes: Origin, Characteristics, and Isolation
A brief overview discussing the differences between exosomes and other extracellular vesicles, therapeutic potential of exosomes, and the difficulties in purifying exosomes. Read More

Review: Therapeutic Effect of L. helveticus (SBT2171) on Collagen-Induced Arthritis
Review of Yamashita et al. (2017) that highlights the therapeutic effect of L. helveticus (SBT2171) on collagen-induced arthritis in mice. Read More

New Product Alert: CD63, CD9, PD-1, PD-L1 Monoclonal Antibodies
Nearly 35 years ago when endosomal-derived extracellular vesicles were first identified in reticulocytes1, they were thought to essentially be garbage cans for the cell; removing cellular debris and marking it for degradation by lysosomes. After this discovery, these vesicles were identified in nearly all mammalian cell types, as well as in some eukaryotes and prokaryotes. However, the function of these molecular vehicles was... Read More

New Product Alert: Mouse Anti-HDM IgE Antibody Assay Kit
A 2013 report from the Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) estimates 39.5 million Americans have been diagnosed with asthma in their lifetimes, with the prevalence of asthma having increased by 28% from 2001-20111. Furthermore, a 2011 report from the National Center for Health Statistics estimated that in 2007 alone, asthma accounted for $56 billion dollars (in 2009 dollars)... Read More

The Hygiene Hypothesis, the Naive Immune System and House Dust Mites
Over the past several decades, many countries around the world have experienced rapid industrialization, leading to increased living standards and improved hygienic measures. While these all seem like positive changes for a society, researchers are finding that these trends have been accompanied by an increase in the prevalence of allergies and autoimmune diseases. Researchers propose that one possible explanation for this phenomenon... Read More

Review: Naive CD4+ T-cells in Autoimmunity & Inflammation
Autoimmunity is attributed to a dysregulation of the adaptive immune response that results in targeting of the bodys own healthy tissues by immune cells. The exact origins of autoimmune responses remain elusive, but a combination of genetic1 and environmental factors2 appear to contribute to the pathogenesis of various autoimmune diseases (ADs). Further adding to this complexity is the various cell types and... Read More