
Type I & Type II Collagen: Structure Influences Staining Patterns
Fibrillar collagens have a unique structure that influence collagen sample preparation and the immunostaining patterns of collagen samples. As such, understanding collagen structure is vital for interpreting SDS-gel and Western Blot results. Here, Chondrex, Inc. scientists share important information about collagens structure and its implications for collagen immunostaining. Read More

Ovalbumin Epitopes in Cell-Mediated Immunity, Humoral Immunity, and Anti-OVA Monoclonal Antibodies
Ovalbumin has long been used as an antigen in pre-clinical allergic disease research. To better understand how ovalbumin immunizations influence immune responses, extensive research has been done to identify T-cell and B-cell epitopes of Ovalbumin. This blog discusses the significance of various OVA epitopes for cell-mediated and humoral immune responses. Read More

Ovalbumin: Ideal Model Antigen for Immunology Research
Ovalbumin (OVA), the primary egg white allergen in infants, was used extensively in early immunology studies investigating antibody-antigen interactions. This historical usage, along with the commercial availability of purified OVA and Anti-OVA Antibody Detection Kits, has OVA a convenient and cost effective model antigen for a variety of research topics: IgE-mediated allergies, vaccines, and oncology. Read this blog to learn more! Read More

Troubleshooting the Collagen-Induced Arthritis Model
While the Collagen-Induced Arthritis model is the most popular rheumatoid arthritis model, there are many sources of variation that can alter the development of the model. Here is a list of factors to consider when planning a CIA experiment in order to reduce sources of variation and increase the reproducibility of your model. Read More

Microbiota: Linking Genetics and Inflammatory Disease
Humans and the microbiota living in an on human surfaces (microbiota) have co-evolved over thousands of years, affecting each other's development in unknown ways. While microbes have traditionally been viewed as having a commensal or parasitic relationship with their hosts, a surge in microbiota research is showing how important microbiota is for human health (1,2). Colonization of human mucosal surfaces... Read More

Arthritis Models: Using CIA and CAIA to Study RA GWAS Risk Loci
Genome Wide Association Studies (GWASs) have identified numerous genes as potential therapeutic targets for rheumatoid arthritis and other autoimmune diseases. However, determining the roles of these genetic factors in RA pathogenesis is virtually impossible. Therefore, the mouse Collagen-Induced Arthritis and Collagen Antibody-Induced Arthritis models are useful tools to parse a genetics mechanisms for autoimmune arthritis. Read More

Review: Naive CD4+ T-cells in Autoimmunity & Inflammation
Autoimmunity is attributed to a dysregulation of the adaptive immune response that results in targeting of the bodys own healthy tissues by immune cells. The exact origins of autoimmune responses remain elusive, but a combination of genetic1 and environmental factors2 appear to contribute to the pathogenesis of various autoimmune diseases (ADs). Further adding to this complexity is the various cell types and... Read More

Tools to Study the Pathological Effect of Human Microbiota in Rheumatoid Arthritis
An overview of murine arthritis models ideal for studying the pathological effects of bacteria and bacterial toxins in the development of rheumatoid arthritis. Read More

Microbiome LPS Heterogeneity Contributes to Autoimmunity
There has been a drastic increase in the incidence of autoimmune diseases (ADs) in industrialized nations versus non-industrialized nations over the past several decades (1). Industrialization is often associated with several consequences: improved medical care, better hygiene, and higher standards of living. These factors work together to lower the infection rate, and therefore the microbial exposure, within the country's population.... Read More
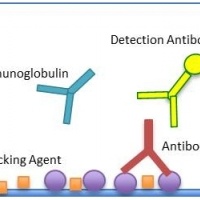
ChonBlock™: A Solution to False Positive Reactions in ELISA
An overview of non-specific reactions in indirect ELISA that can lead to false positive results. Read More
1 to 10 of 10